The following image illustrates the Content Management - Articles|Text page:
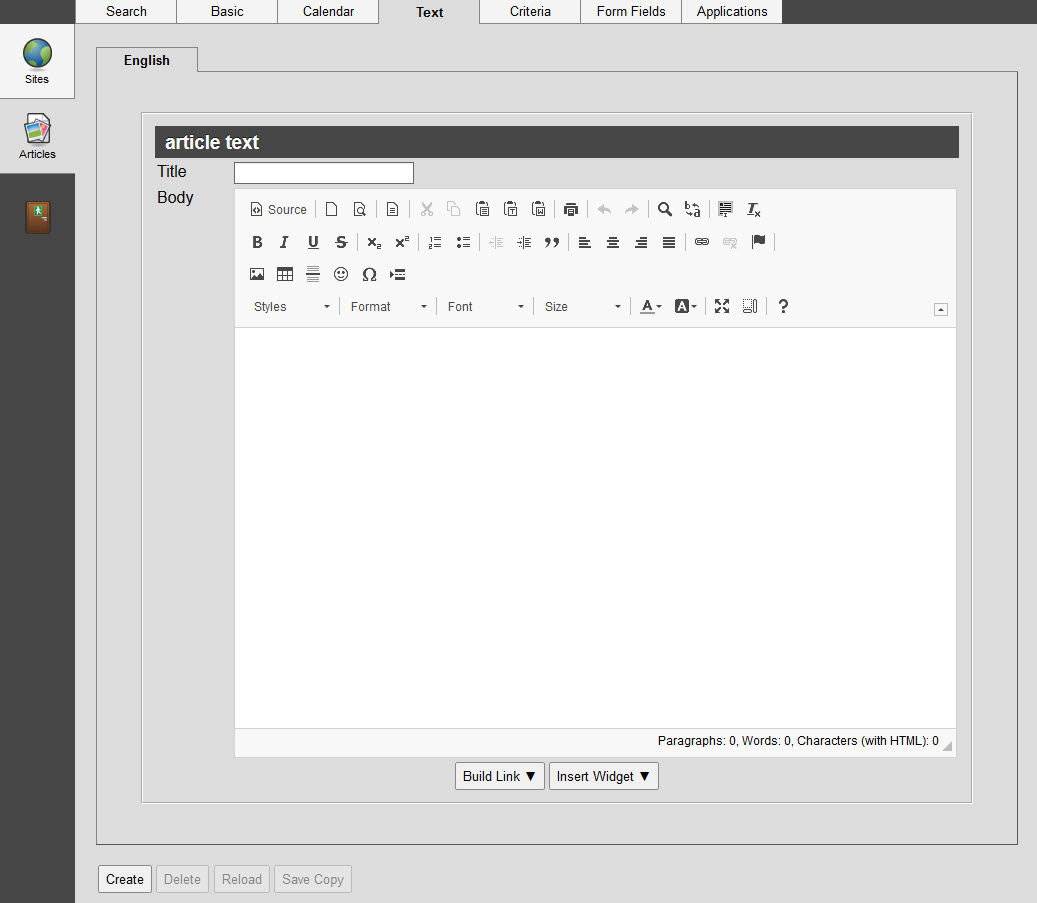
The Articles|Text page allows you to construct the content of the selected article that will be read by the user.
You can create an article using the rich text and source editors. The rich text editor allows you to format your article using standard typographical effects (bold, italics, underline, strikethrough), bullets, text alignment, several fonts and font sizes. You can also insert tables, images and URLs to direct readers to other related sites or specific on-sale items. You can also view/edit the HTML source code.
The editor also provides a few templates to choose from to assist you in formatting your article easily.
The Content Management - Articles|Text page contains the following properties:
Field |
Description |
Title |
Enter a title for the article. |
Meta Description |
Enter a description for the article. This will ensure that the description written here will be viewed on the page for the online version of the article in HTML. The value entered in this field will also be used in conjunction with the Facebook Like button if an Open Graph Description value has not been set on the Site|Applications or Article|Applications pages. |
Body |
Using the rich text and source editors, enter the content of your article. |
The following table describe the various buttons that appear on the Articles|Text page:
Button |
Description |
Allows you to build and insert links to specific events and items. |
|
Allows you to insert various widgets into articles. |
|
Allows you to create templates by inserting fields that will pull information configured against events, bundles, miscellaneous items, gifts, stored value items and event owner profiles. If you do not select Template or Template with Search from the 'Type' dropdown on the Article|Basic page, the button will not appear. |
|
Allows you to insert form fields into articles to create surveys and feedback forms. If you do not create a form field, the button does not appear. |
For more information, refer to Primary Feature Article Images and Secondary and Tertiary Feature Article Images.